Derivatives: A Wrap Up
To wrap up our work with derivatives, I’ve included a set of free response questions for every major topic involving limits, continuity, and derivatives. Go through these problems for review. The answer key and explanations for all of the problems on this page can be found [here].
Limits and Continuity
Problem 1
This problem is adapted from SAUSD.
The graph of the function $f$ is shown in the $xy$-plane below.
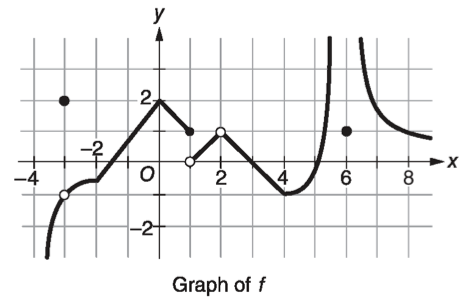
$f$ has a discontinuity due to a vertical asymptote at $x=6$. Let $g$ be a function that is continuous and increasing for all $x$. Values of $g(x)$ at selected values of $x$ are shown in the table below.
| $x$ | -0.2 | -0.1 | -0.01 | -0.001 | 0.001 | 0.01 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| $g(x)$ | 1.975 | 1.988 | 1.997 | 1.999 | 2.001 | 2.003 | 2.012 | 2.025 |
- Using the graph of $f$ and the table for $g$, estimate \(\lim_{x\rightarrow 0}\left[f(x)-g(x)\right]\).
- For each value of $a=1, a=2, a=4, a=6$, find $\lim_{x\rightarrow a}f(x)$ or explain why $\lim_{x\rightarrow a}f(x)$ does not exists. Use correct limit notation in your answers.
- If $f$ continuous at $x=-3$? Using correct limit notation, justify your answer.
- Write a difference quotient that best approximates the instantaneous rate of change of $g$ at $x=0$.
Problem 2
This problem is adapted from SAUSD.
Let $f$ be the function defined by $f(x)=\frac{ax^2+bx+2}{2x^2-8}$, where $a$ and $b$ are constants. The graph of $f$ has a horizontal asymptote at $y=3$, and $f$ has a removable discontinuity at $x=2$.
- Find $a$ and $b$.
- To make $f$ continuous at $x=2$, $f(2)$ should be defined as what value? Justify your answer.
- At what value of $x$ does $f$ has a discontinuity due to a vertical asymptote? Give a reason for your answer.
Problem 3
This problem is adapted from SAUSD.
The number of fish in a pond at time $t$ years is modeled by the function $N$ defined as
\[N(t)=\begin{cases} f(t) & \text{for }0\leq t<6 \\ 25t+150 & \text{for }6\leq t<8\\ \frac{200+80t}{2+0.05t} & \text{for }t\geq 8\end{cases}\]Here, $f$ is a continuous function with $f(0)=80$.
- Find $\lim_{t\rightarrow \infty}N(t)$. Explain the meaning of $\lim_{t\rightarrow \infty}N(t)$ in the context of the problem.
- Is the function $N$ continuous at $t=8$? Justify your answer.
- The function $N$ is continuous at $t=6$. Is there a time $t$, for $0\leq t\leq 6$, at which $N(t)=250$? Justify your answer.
Problem 4
Let $f$ be the function as defined below:
\[f(x)=\begin{cases}\frac{x^2-4}{x-2} & \text{if }x\neq 2 \\ 1 & \text{if }x=2 \end{cases}\]Which of the following statements about $f$ are true?
- $f$ has a limit at $x=2$.
- $f$ is continuous at $x=2$.
- $f$ is differentiable at $x=2$.
Differentiation: Definition and Basic Derivative Rules
Problem 1
This problem is adapted from the 2004 AP Calculus AB Exam.
Traffic flow is defined as the rate at which cars pass through an intersection, measured in cars per minute. The traffic flow at a particular intersection is modeled by the function $F$ defined by
\[F(t)=82+4\sin\left(\frac{t}{2}\right)\text{ for }0\leq t\leq 30\]where $F(t)$ is measured in cars per minute and $t$ is measured in minutes.
- Is the traffic flow increasing or decreasing at $t=7$? Give a reason for your answer.
- What is the average rate of change of the traffic flow over the time interval $10\leq t \leq 15$? Indicate units of measure.
- Is the Mean Value Theorem (MVT) applicable in this problem over the entire interval $0\leq t\leq 30$ for this function $F(t)$? If yes, find the particular time points $t$ where the instantaneous rate of change of $F(t)$ is equal to the average rate of change of $F(t)$. If no, explain why not.
Problem 2
This problem is adapted from the 2007 AP Calculus AB Exam.
The wind chill is the temperature, in degrees Fahrenheit $^{\circ}$F, a human feels based on the air temperature, in degrees Fahrenheit, and the wind velocity $v$, in miles per hour (mph). If the air temperature is 32$^{\circ}$F, then the wind chill is given by
\[W(v)=55.6-22.1v^{0.16} \text{ for }5\leq v \leq 60\]- Find $W’(20)$. Using correct units, explain the meaning of $W’(20)$ in terms of the wind chill.
- Find the average rate of change of $W$ over the interval $5\leq v\leq 60$. Find the value of $v$ at which the instantaneous rate of change of $W$ is equal to the average rate of change of $W$ over the interval $5\leq v\leq 60$.
- Over the time interval $0\leq t\leq 4$ hours, the air temperature is a constant 32$^{\circ}$F. At time $t=0$, the wind velocity is $v=20$ mph. If the wind velocity increases at a constant rate of $5$ mph per hour, what is the rate of change of the wind chill with respect to time at $t=3$ hours? Indicate units of measure.
Problem 3
This problem is adapted from the 1999 AP Calculus AB Exam.
In the figure below, line $\ell$ is tangent to the graph of $y=\frac{1}{x^2}$ at point $P$, with coordinates $\left(w, \frac{1}{w^2}\right)$, where $w>0$. Point $Q$ has coordinates $(w, 0)$. Line $\ell$ crosses the $x$-axis at point $R$, with coordinates $(k, 0)$.
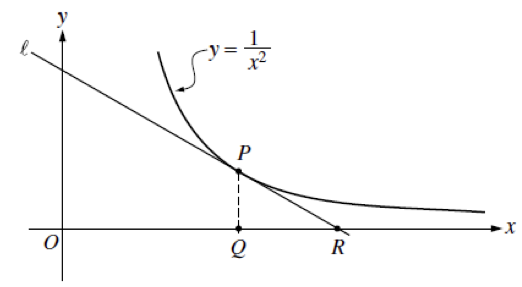
Answer the following questions.
- Find the value of $k$ when $w=3$.
- For all $w>0$, find $k$ in terms of $w$.
- Suppose that $w$ is increasing at a constant rate of $7$ units per second. When $w=5$, what is the rate of change of $k$ with respect to time?
- Suppose that $w$ is increasing at a constant rate of $7$ units per second. When $w=5$, what is the rate of change of the area of $\Delta PQR$ with respect to time? Determine whether the area is increasing or decreasing at this instant.
Problem 4
Suppose that $f(x)$ is some differentiable function. Differentiate the following two functions:
- \[y=\frac{1+xf(x)}{\sqrt{x}}\]
- \[y=\frac{\sqrt{x+f(x)}}{f^2(x)}\]
Problem 5
If $y\cos(x^2+1)=x\sin(y^2+1)$, then use implicit differentiation to find (a) $\frac{dx}{dy}$, and (b) $\frac{dy}{dx}$.
Problem 6
A particle moves in a straight line along the $x$-axis. Its displacement is given by the function $s(t)=3t^3-8t^2+12t+6$ for $t\geq 0$, where $t$ is measured in seconds and $s$ is measured in meters.
- Find the velocity function of the particle at time $t$.
- Find the acceleration function of the particle at time $t$.
- Find all of the times $t$ when the particle turns around to the other direction. What is the position of the particle at these times $t$? Is the particle traveling left and then turns to the right, or traveling right and then turns to the left at these times $t$?
Differentiation: Composite, Implicit, and Inverse Functions
Problem 1
This problem is adapted from Khan Academy.
Let $f$ and $h$ be inverse functions. The following table lists a few values of $f$, $h$, and $f’$:
| $x$ | $f(x)$ | $h(x)$ | $f’(x)$ |
| -4 | 2 | 1 | 1/3 |
| 1 | -4 | -2 | 4 |
What is $h’(-4)$?
Problem 2
This problem is adapted from the 2015 AP Calculus AB Exam.
Consider the curve given by the equation $y^3-xy=2$.
- What is $\frac{dy}{dx}$?
- Write an equation for the line tangent to the curve at the point $(-1, 1)$.
- Find the coordinates of all points on the curve at which the line tangent to the curve at that point is vertical.
- Evaluate $\frac{d^2y}{dx^2}$ at the point on the curve where $x=-1$ and $y=1$.
Problem 3
This problem is adapted from the 1998 AP Calculus AB Exam.
Consider the curve defined by $2y^3+6x^2y-12x^2+6y=1$.
- What is $\frac{dy}{dx}$?
- Write an equation of each horizontal tangent line to the curve.
- The line through the origin with slope -1 is tangent to the curve at point $P$. Find the $x$ and $y$ coordinates of point $P$.
Contextual Applications of Differentiation
Problem 1
A 50 ft ladder is placed against a large building. The base of the ladder is resting on an oil spill, and it slips at the rate of 3 ft per minute. Find the rate of change of the height of the top of the ladder above the ground at the instant when the base of the ladder is 30 ft from the base of the building.
Problem 2
A spherical balloon is being inflated so that its diameter is increasing at a rate of 2 cm per min. How quickly is the volume of the balloon increasing when the diameter is 10 cm?
Problem 3
A person who is 6 feet tall is walking away from a lamp post at the rate of 40 feet per minute. When the person is 10 feet from the lamp post, his shadow is 20 feet long. Find the rate at which the length of the shadow is increasing when he is 30 feet from the lamp post.
Problem 4
A rectangular page is to contain 24 square inches of print. The margins at the top and bottom of the page are each 1.5 inches. The margins on each side are 1 inch. What should the dimensions of the page be so that the least amount of paper is used?
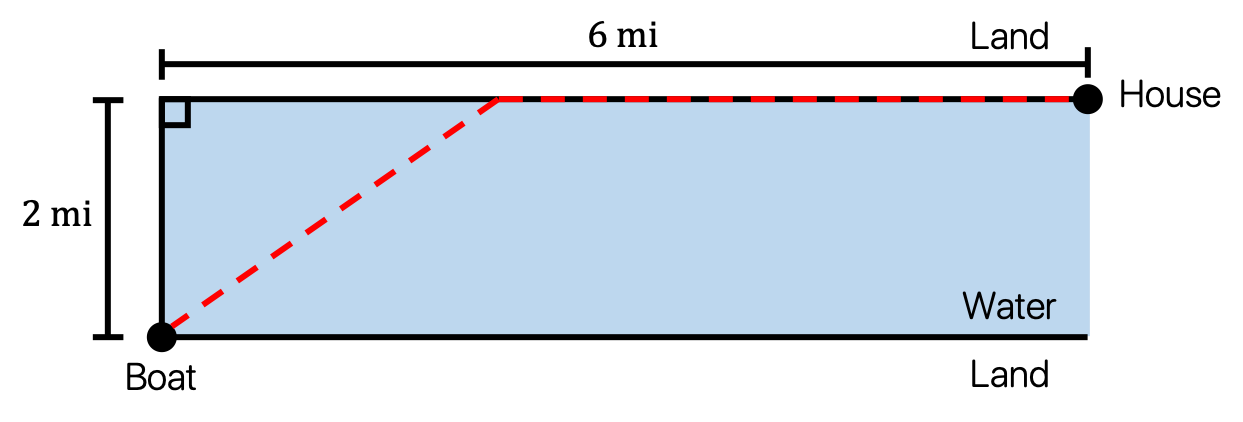
Problem 5
A person in a row board two miles from the nearest point on a straight shoreline wishes to reach a house six miles farther down the shore. If the person can row at a rate of 3 miles per hour and walk at a rate of 5 miles per hour, find the least amount of time required to reach the house. How far from the house should the person land the rowboat?